Microlearning Examples:
Empowering Employees Effectively
In the fast-paced world of business, effective knowledge transfer is crucial.
Traditional training methods often hit their limits. This is where microlearning, with its short, animated videos, offers an efficient solution for quickly and sustainably imparting knowledge.
Challenges of traditional employee training
1. Time-Consuming: The learning process often takes a lot of time
2. Costly: Training can incur high expenses
3. Forgetfulness: Learned knowledge is often quickly forgotten
4. Resource-Intensive: Creating training units requires significant resources
Advantages of Microlearning
1. Short Learning Units: Easy to grasp and understand content that is better retained
2. Practical Application: Knowledge that can be immediately used in everyday work
3. Flexibility: Content can be easily and conveniently reviewed anytime
4. Up-to-Date: It is easy to update content
4. Multilingual: Learning content that is well understood in different languages
Microlearning – Learn quickly and easily!
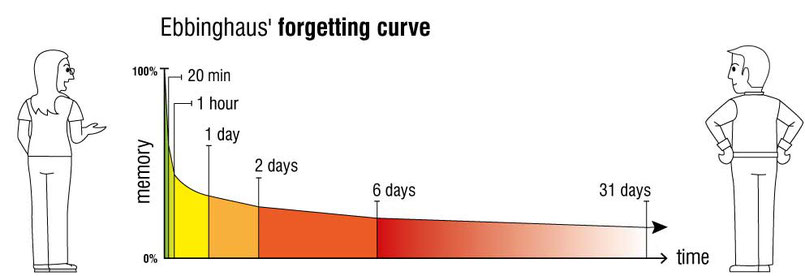
Prof. Ebbinghaus forgetting curve
The forgetting curve was researched and described by Hermann Ebbinghaus, a German psychologist, at the end of the 19th century. His groundbreaking experiments laid the foundation for understanding human memory and influenced many teaching and learning methods, including the concept of microlearning.
He found that within an hour of learning, about half of what was learned was forgotten. After one day it was already over 70%, and after a month the proportion of things forgotten rose to around 90%. This shows how quickly pieces of content are lost again.
Microlearning = Learning in Small Units
Microlearning, also known as “bit-sized learning”, is an innovative teaching and learning method that aims to impart knowledge and skills in small, easily digestible bites. Typically, the content is presented in the form of infographics, short e-learning lessons, videos, and quiz questions that usually last only a few minutes, often with interactive elements.
In a corporate context, microlearning is used to train employees efficiently and effectively. It allows them to quickly access relevant information and immediately apply it to their work. This flexible and time-efficient learning strategy helps shorten the learning curve and empowers employees to take on new tasks.
Microlearning Examples

How Microlearning Promotes Sustainable Learning
In the B2B world, clear communication is crucial. Difficult-to-understand topics are often the norm, be it when introducing new technologies or explaining sophisticated business models. In this environment, it is essential to reduce this complexity and simplify the topics so that everyone can understand them.
To minimize forgetting and effectively training employees, consider these strategies:
- Regular Repetition: Ensure regular refreshers of the learned material
- Practical Application: Encourage direct application of knowledge in the workplace
- Interactive Methods: Use interactive learning formats to enhance engagement and retention
- Personalized Learning: Tailor content to meet individual needs
- Feedback and Evaluation: Implement regular feedback and evaluation systems to monitor learning success
What is the Concept behind Microlearning?
Microlearning is an efficient training method that delivers knowledge to employees in short, precise units without disrupting their daily work.
Companies use microlearning to flexibly and continuously expand their employees' skills. For example, through 2-3 minute learning videos and interactive tasks on new software tools or soft skills. The content is specifically tailored to the employees' needs and covers a wide range of topics. The more complex your topic is, the more important it is that it is comprehensible to your audience.

Challenges of Microlearning in a Company
Introducing microlearning in a company can come with its set of challenges. Here are some of the key hurdles:
Acceptance and Cultural Shift: The biggest challenge often lies in overcoming resistance to new learning methods. It’s crucial to foster a learning culture that supports open and self-directed learning.
Technology and Infrastructure: Companies need to ensure they have the necessary technological infrastructure to make microlearning content accessible. This includes compatible hardware, an appropriate learning platform, and reliable internet connections.
Content Development: Creating high-quality, targeted content in short formats can be demanding. It requires specialized skills in content creation and instructional design.
Measuring Learning Success: It can be challenging to measure the success of microlearning, as traditional assessment methods might not be suitable. Companies need to develop effective tools for evaluating and monitoring digital learning progress.
Employee Motivation: Keeping employees engaged and motivated to regularly interact with microlearning units is crucial.
By addressing these challenges, microlearning can become an effective and flexible learning method in the corporate world, enabling employees to continuously and efficiently acquire new knowledge and skills.

Microlearning – The Secret Weapon for Efficient and Flexible Employee Learning
Time Efficiency: By delivering short learning content as brief videos, learners can acquire knowledge in less time. This helps achieve learning objectives more efficiently and boosts productivity within the company.
Increased Engagement: Short and concise microlearning units are more accessible and engaging. They help maintain motivation and attention throughout the learning process.
Improved Knowledge Retention: Regular repetition and application of learned material enhance knowledge retention. The bite-sized learning units make it easier for learners to remember and apply the information.
Mobile Learning: Microlearning offers the flexibility to learn anytime, anywhere. With mobile devices, learners can access content on the go, further increasing learning efficiency and accessibility.
Support for Self-Directed Learning: Microlearning’s short, customizable units allow learners to choose their own learning path and control their pace. This fosters a sense of autonomy and responsibility in the learning process.
Personalized Learning: Microlearning can be easily tailored to individual needs and learning styles. By providing customized content, learners can focus on their specific interests and goals, leading to more effective knowledge acquisition.

8 Benefits of
Microlearning:
Microlearning means Cost Savings and
Maximized Learning Outcomes for Companies
1. Comparing Costs: Microlearning vs. Traditional Training
Traditional training formats like workshops
or seminars often involve significant expenses for trainers, facilities, and travel. Microlearning, on the other hand, drastically reduces these costs by relying on digital platforms and
providing brief, targeted content.
2. Financial Benefits of Implementing Microlearning
Adopting microlearning not only cuts direct training costs but also optimizes time spent on training, reducing indirect costs such as lost work hours.
Simplifying Knowledge Transfer – one of the Advantages of Microlearning
3. How Microlearning Streamlines Knowledge Delivery
Microlearning delivers knowledge quickly and
effectively through short, focused units tailored to specific needs and readily accessible at any time.
4. Rapid Development and Updates
Microlearning content is not only quick to develop but also easy to update. This ensures that information and technology remain up-to-date.
Workplace Learning / Mobile Learning
5. Applications in Formal and Informal Learning
Microlearning is versatile and can be applied in both
formal training programs and informal learning situations, making it a valuable tool for employee development.
6. Utilization Across Different Learning Environments
Whether at the workplace, on the go, or at home, microlearning units can be used in various settings to support continuous learning.
Microlearning Strategy
7. Speed of Reaching Learning Goals
Microlearning enables learners to achieve specific learning
objectives quickly and efficiently by focusing on the immediate application of knowledge.
8. Improving ROI of Training Initiatives
By streamlining learning processes and minimizing downtime, microlearning enhances the return on investment (ROI) for training programs.
In the long run, microlearning boosts individual performance, adaptability, and innovation within the company, leading to sustained success.

Creating Animated Microlearning Videos in 7 Steps
To transform learning materials into animated learning videos for effective microlearning, follow these steps:
1. Define Goals: Determine the skills, knowledge, or specific topics to be conveyed. Clarify the learning objective to tailor the content accordingly, considering the target audience and their prior knowledge.
2. Develop a Storyboard: Create a storyboard that visually outlines how the storytelling will be translated into animated scenes. This helps plan the flow of the video and effectively use visual elements. Additionally, the text for the speaker should be clear, concise, and to the point.
3. Choose Tools: Select an animation software that meets your needs. Popular options include Adobe After Effects, Vyond, or Animaker.
4. Animate: Use the software to animate the scenes planned in the storyboard. Integrate text, images, and characters that support the message.
5. Add Audio: Record the voice-over with a clear and articulate voice. Good audio quality is crucial for understanding. Background music can be added but should not be distracting.
6. Gather Feedback and Adjust: Show the video to a test group to collect feedback. Use the feedback to make improvements to the video.
7. Publish and Monitor: Make the video available to your employees and monitor its usage. Collect further feedback and adjust your learning video as needed to maximize effectiveness.
By following these steps, you can create animated learning videos that are not only informative but also engaging for your employees.
Creating Microlearning Modules

Studies show that microlearning can increase learning efficiency by up to 50% by providing short, concise units tailored to the learners' capacity and attention span.
Feel free to schedule a meeting with us to discuss the topic or send us an email to learn more about microlearning.

We recommend the following literature on this topic:

"Microlearning: Short and Sweet" Karl M. Kapp and Robyn A. Defelice
This book provides a comprehensive introduction to the concept of microlearning. The authors, both seasoned educators and consultants, demystify microlearning by discussing practical applications and case studies. They define microlearning as brief learning units designed to achieve specific outcomes and offer a detailed guide to planning, implementing, and evaluating microlearning strategies. This book is especially useful for learners and designers looking to apply microlearning in various contexts.

"The Microlearning Guide to Microlearning" by Carla Torgerson and Sue Iannone
This book focuses on the practical application of microlearning in the corporate world. It offers readers actionable tips and techniques for designing and implementing effective microlearning. The authors explain how microlearning can enhance learning retention and improve employee performance, and discuss various formats and methods that can be applied in real work environments.

"Didactics of Microlearning" edited by Theo Hug
This book explores the uses and effectiveness of microlearning, a teaching method that employs brief information units to optimize learning. It covers theoretical foundations, practical applications, and case studies demonstrating how microlearning can be effectively implemented in different educational contexts.